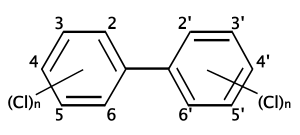
Figure: Molecular structure of PCB
ALS offering for PCB testing
|
Matrix |
LOQ |
Sample volume |
|
Soil/Sediment |
1 pg/g dw WHO2005-TEQ 17 ng/g dw sum of 7PCBs |
5 g |
|
Ash |
3.5 pg/g dw WHO2005-TEQ 17 ng/g dw sum of 7PCBs |
2 g |
|
Sludge/waste |
11 pg/g dw WHO2005-TEQ 17 ng/g dw sum of 7PCBs |
1 g |
|
Water |
1.5 pg/L WHO2005-TEQ 68 ng/L sum of 7PCBs |
1 L |
|
Air |
7 pg/sample TEQ-dl-PCB 17 ng/sample of 7PCBs |
|
|
Biota - food |
LOQ< 1/5 of maximal levels according to Commission Regulation (EU) No 1259/2011 |
|
|
Biota - feed |
LOQ< 1/5 of maximal levels according to Commission Regulation (EU) No 277/2012 |
|
|
Clinical samples (Blood, serum) |
5 pg/g of fat WHO2005-TEQ 100 ng/g of fat sum of 6PCBs |
For 50 g of blood sample or for 30 g of serum |
OVERVIEW
German scientists first synthesized PCB as far back as 1881, and for the following nearly 100 years PCB was produced and sold as a commercial product. The physical and chemical properties of PCB makes it useful for several applications but the same properties is also the reason why PCB can be found in the environment even today.
PCB is very stable both chemically and thermally and has a high dielectric constant. The properties makes PCB an attractive compound for a number of applications:
- Added to insulating fluid for transformer but also to other types of oil (closed applications)
- Used in carbonless copy paper
- Plasticiser in paints
- Additive in flexible PVC coating
- Softener in sealants and coal tar
Toxicity
All PCB congeners, 209 in total, are lipophilic and will accumulate in the food chain. The toxicity of PCB varies depending on degree of chlorination and structure of the molecule. Some PCB’s, called co-planar PCB’s, have similar structure and toxicity to dioxins.
PCB has been classified as likely carcinogenic. It can cause development defects, disrupt hormone function and negatively affects immune system and thyroid function.
Table: International threshold values for PCB
|
Country |
Matrix |
Limit |
|
Czech Republic |
Water |
0,012 µg/l-1 |
|
Czech Republic |
Soil |
0,02 mg/kg-1 DW |
|
Denmark |
Air |
300 -3000 ng/m3 |
|
Denmark |
Sediment |
20 - 200 µg/kg |
|
Turkey |
Air |
0,1 ng/Nm3 |
|
Turkey |
Water |
0,07 µg/L (0,01 µg/L individually) |
|
Turkey |
Sludge |
0,8 mg/kg DW |
|
Turkey |
Soil |
0,003 mg/kg |


